Weather and climate are two important aspects of Earth’s atmosphere that influence our daily lives and shape the environment around us. Understanding the differences between weather and climate helps us comprehend how the atmosphere behaves over short and long periods of time.
Weather:
Weather refers to the day-to-day changes in atmospheric conditions such as temperature, humidity, precipitation (rain, snow, sleet), wind speed, and cloud cover. It describes what is happening in the atmosphere at a specific place and time. Weather conditions can change quickly and vary from one location to another. For example, one day might be sunny and warm, while the next day could be cloudy and rainy.
Factors that influence weather include:
– Temperature: The amount of heat in the atmosphere, which affects how warm or cold it feels.
– Humidity: The amount of moisture or water vapor in the air, which influences how muggy or dry it feels.
– Pressure: Air pressure changes can indicate the likelihood of fair weather or storms.
– Wind: Movement of air from high-pressure areas to low-pressure areas, influencing temperature and precipitation patterns.
– Clouds: Cloud cover affects how much sunlight reaches the Earth’s surface and can indicate impending weather changes.
Climate:
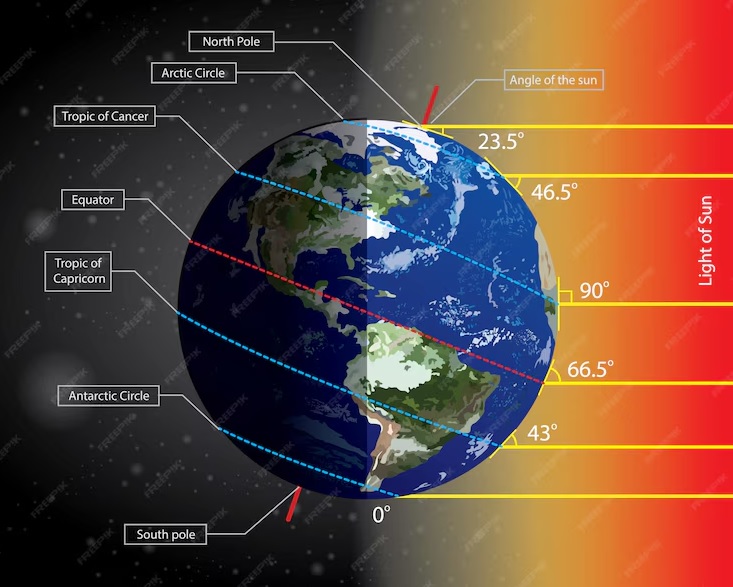
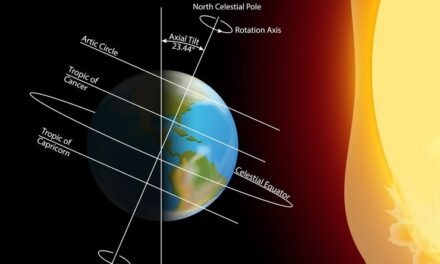
Climate refers to the long-term patterns and averages of weather conditions in a particular region over many years. It provides a broader perspective of the typical weather patterns, seasonal variations, and trends in temperature and precipitation that characterize a specific area. Climate is determined by factors such as latitude, altitude, proximity to oceans or mountains, and prevailing wind patterns.
For example, regions near the equator generally have a tropical climate with warm temperatures year-round and frequent rainfall, while polar regions have a cold climate with long winters and short summers.
Understanding weather and climate helps us predict and prepare for different atmospheric conditions, whether it’s planning outdoor activities, farming, or managing natural disasters like hurricanes or droughts. Scientists study weather and climate using instruments such as thermometers, barometers, satellites, and weather balloons to gather data and make forecasts.
In conclusion, weather and climate are fundamental aspects of Earth’s atmosphere that impact our daily lives and shape ecosystems around the world. By learning about these concepts, we gain insights into the dynamics of our planet’s atmosphere and how human activities can influence weather patterns and climate change over time.
The worksheet covers the following topics: –
What is climate?
What influences climate
Distance from the Equator
Height above the sea level (altitude)
Distance from the sea
Direction of winds
Humidity and Rainfall
Heat Zones
Torrid Zone
Temperate Zone
Frigid Zone