Clean Surroundings
Chapter 12: Keeping Our Surroundings Clean
Welcome to an important chapter about keeping our surroundings clean! Clean environments are essential for our health and happiness. In this chapter, we’ll explore how to manage different types of waste to keep our surroundings neat and healthy. We’ll cover the disposal of solid and liquid wastes, and learn about biodegradable and non-biodegradable waste. Let’s get started on our journey to a cleaner world!
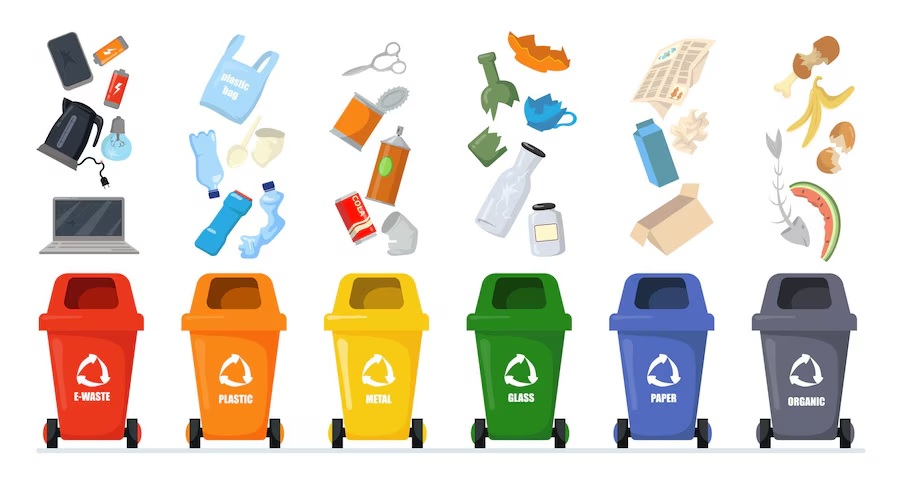
Disposal of Solid Wastes
Solid waste includes everything that people throw away that is solid, like food scraps, paper, plastic, and metal. Proper disposal of solid waste helps keep our environment clean and prevents pollution.
What is Solid Waste?
Solid waste consists of materials we discard because we no longer need them or they are broken. These can be:
– Household Trash: Items like food scraps, old newspapers, broken toys, and packaging.
– Garden Waste: Leaves, grass clippings, and branches.
– Industrial Waste: By-products from factories, like metal scraps or leftover materials from manufacturing processes.
How to Dispose of Solid Waste
There are several methods for disposing of solid waste properly:
- Recycling:
– Description: Recycling involves collecting, processing, and reusing materials like paper, glass, plastic, and metal.
– Example: Paper is recycled to make new paper products; plastic bottles are turned into new plastic items.
- Composting:
– Description: Composting is a natural process of recycling organic waste, like food scraps and yard waste, into valuable fertilizer.
– Example: Fruit and vegetable peels, coffee grounds, and grass clippings can be composted to create nutrient-rich compost for gardens.
- Landfills:
– Description: Landfills are sites where waste is buried. This is usually used for non-recyclable and non-compostable waste.
– Example: Non-recyclable plastics and certain types of industrial waste.
- Incineration:
– Description: Incineration involves burning waste at high temperatures. This method reduces the volume of waste but can produce smoke and pollutants.
– Example: Some types of municipal solid waste are incinerated to reduce the amount of landfill space needed.
Biodegradable Waste
Biodegradable waste is organic matter that can be broken down by natural processes into simpler substances. This type of waste decomposes over time and can be turned into compost.
What is Biodegradable Waste?
Biodegradable waste includes materials that are broken down by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. Examples are:
– Food Waste: Fruit peels, vegetable scraps, and leftover food.
– Yard Waste: Grass clippings, leaves, and small branches.
– Paper Products: Cardboard and newspapers.
How to Manage Biodegradable Waste
- Composting:
– Description: Composting biodegradable waste helps turn it into nutrient-rich compost that can be used to enrich soil.
– Example: Kitchen scraps and garden waste can be composted in a home compost bin or pile.
- Green Waste Collection:
– Description: Some communities have special collection services for biodegradable waste that is collected separately from regular trash.
– Example: Yard waste bins provided by local waste management services.
Non-Biodegradable Waste
Non-biodegradable waste is made up of materials that do not decompose naturally. These materials remain in the environment for a long time and can cause pollution.
What is Non-Biodegradable Waste?
Non-biodegradable waste includes items that cannot be broken down by natural processes. These materials often stay in landfills for many years and can contribute to environmental pollution. Examples include:
– Plastics: Plastic bags, bottles, and packaging.
– Metals: Cans, aluminum foil, and other metal items.
– Glass: Bottles and jars.
How to Manage Non-Biodegradable Waste
- Recycling:
– Description: Many non-biodegradable materials, like plastic, glass, and metal, can be recycled and used to make new products.
– Example: Plastic bottles can be recycled to create new plastic items; glass bottles can be melted down and reused.
- Proper Disposal:
– Description: Items that cannot be recycled should be disposed of properly in landfills or through designated waste collection services.
– Example: Using community drop-off centers for hazardous waste like batteries or electronics.
- Reduce and Reuse:
– Description: Reducing the amount of waste we produce and reusing items helps minimize the impact of non-biodegradable waste.
– Example: Using reusable shopping bags instead of plastic ones and donating old clothes instead of throwing them away.
Disposal of Liquid Wastes
Liquid waste includes any liquid by-products from households, industries, or other sources. Proper disposal of liquid waste is crucial for preventing pollution and protecting water sources.
What is Liquid Waste?
Liquid waste includes substances that are in liquid form and are discarded. Examples are:
– Household Waste: Used cooking oil, cleaning agents, and wastewater from sinks and showers.
– Industrial Waste: Chemicals, solvents, and other by-products from manufacturing processes.
– Sewage: Wastewater from toilets and drains.
How to Manage Liquid Waste
- Wastewater Treatment:
– Description: Wastewater from homes and industries is treated at facilities to remove harmful substances before being released into the environment.
– Example: Municipal wastewater treatment plants process sewage and other wastewater to ensure it is clean before it enters rivers or oceans.
- Proper Disposal:
– Description: Some liquid wastes, especially hazardous ones, need special disposal methods to prevent contamination.
– Example: Used motor oil should be taken to a recycling center that handles hazardous materials.
- Recycling and Reuse:
– Description: Some liquid wastes can be treated and reused, such as wastewater that is recycled for industrial processes.
– Example: Recycled water used for irrigation or industrial cooling.
- Why Clean Surroundings Matter
Keeping our surroundings clean is essential for many reasons:
- Health:
– Description: Proper waste disposal prevents the spread of diseases and reduces pollution that can harm our health.
– Example: Reducing garbage in public spaces helps prevent the spread of germs and pests.
- Environment:
– Description: Clean environments support healthy ecosystems and prevent pollution of air, water, and soil.
– Example: Proper waste management helps keep rivers and lakes free of harmful chemicals and trash.
- Aesthetics:
– Description: Clean surroundings are more pleasant to look at and help create a positive and welcoming community.
– Example: Well-maintained parks and public spaces enhance the beauty of our neighborhoods.
- Resources:
– Description: Efficient waste management helps conserve resources by recycling and reusing materials.
– Example: Recycling reduces the need for new raw materials and helps save energy.
How You Can Help
Everyone can contribute to keeping our surroundings clean. Here are some simple actions you can take:
- Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle:
– Description: Try to reduce the amount of waste you produce, reuse items whenever possible, and recycle materials like paper, plastic, and glass.
– Example: Bring your own reusable water bottle to school instead of using single-use plastic bottles.
- Proper Disposal:
– Description: Dispose of waste properly by following local guidelines and using designated bins for recycling, composting, and trash.
– Example: Separate your recyclables from your regular trash at home.
- Participate in Clean-Up Activities:
– Description: Join community clean-up events or organize one yourself to help keep public spaces clean.
– Example: Participate in a park clean-up day or organize a neighborhood litter pick-up.
- Educate Others:
– Description: Share what you’ve learned about waste management with family and friends to help spread awareness.
– Example: Teach your family how to compost and recycle effectively.
- Review and Quiz
Let’s review what we’ve learned about keeping our surroundings clean:
- What is solid waste?
– Solid waste includes materials we throw away that are solid, like food scraps and plastic.
- What is biodegradable waste?
– Biodegradable waste is organic matter that can decompose naturally, like food scraps and yard waste.
- What is non-biodegradable waste?
– Non-biodegradable waste includes materials that do not decompose naturally, like plastics and metals.
- How should liquid waste be managed?
– Liquid waste should be treated at facilities, properly disposed of, or recycled if possible.
- Why is keeping our surroundings clean important?
– It helps maintain health, protect the environment, improve aesthetics, and conserve resources.
Great job learning about how to keep our surroundings clean! By understanding and practicing proper waste management, you can help make the world a cleaner and healthier place. Keep making a difference and enjoy the beauty of a clean environment. Happy cleaning!
The worksheet covers the following topics-
Disposal of Solid wastes
Biodegradable waste
Non-biodegradable waste
Disposal of Liquid Wastes