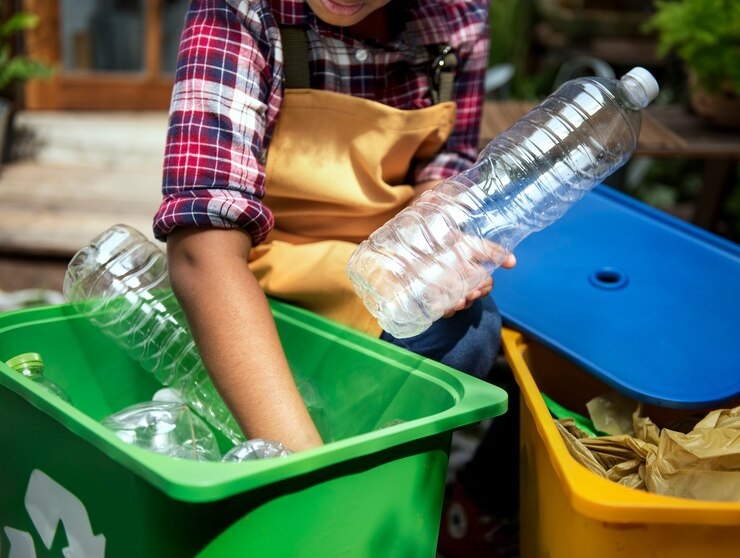
Effective waste management is crucial for protecting the environment, conserving natural resources, and promoting sustainable development. Waste management involves the collection, transportation, disposal, and recycling of waste materials generated by human activities. It plays a vital role in minimizing pollution, reducing greenhouse gas emissions, and preserving ecosystems for future generations.
Types of Waste:
Waste can be categorized into several types based on its source and composition:
- Solid Waste: Solid waste includes household garbage, industrial waste, and construction debris. It can be further classified into biodegradable (organic) waste, such as food scraps and yard trimmings, and non-biodegradable waste, such as plastics and metals.
- Hazardous Waste: Hazardous waste poses risks to human health and the environment due to its toxic, flammable, corrosive, or reactive properties. Examples include batteries, electronic waste (e-waste), and chemical solvents.
- Medical Waste: Medical waste from healthcare facilities includes infectious materials like needles, syringes, and contaminated dressings. Proper disposal is essential to prevent the spread of diseases and protect public health.
Environmental Impact:
Improper waste management can lead to various environmental and health hazards:
– Land Pollution: Improper disposal of solid waste can contaminate soil and groundwater, affecting plant growth and drinking water quality. Plastic waste, in particular, persists in the environment for centuries, harming wildlife and marine ecosystems.
– Air Pollution: Open burning of waste releases harmful pollutants, including particulate matter and toxic gases like dioxins and furans. These pollutants contribute to respiratory diseases and climate change.
– Water Pollution: Improperly managed waste can leach harmful chemicals into water bodies, contaminating aquatic habitats and threatening marine life. Effluents from industries and untreated sewage discharge are major sources of water pollution.
Waste Management Strategies:
To address these challenges, waste management strategies focus on reducing waste generation, promoting recycling and reuse, and implementing safe disposal methods:
- Source Reduction: Minimize waste generation by adopting practices such as composting organic waste, reducing packaging, and promoting reusable products.
- Recycling: Collect and process recyclable materials like paper, glass, metals, and plastics to conserve natural resources and reduce energy consumption.
- Waste-to-Energy: Convert non-recyclable waste into energy through technologies like incineration and anaerobic digestion, reducing landfill waste and generating electricity or heat.
- Landfill Management: Properly design and manage landfills to prevent groundwater contamination and methane emissions. Implement landfill gas recovery systems to capture methane for energy production.
- Regulations and Education: Enforce regulations on waste disposal practices and educate communities about the importance of responsible waste management. Encourage public participation through waste separation and recycling programs.
Conclusion:
Effective waste management is essential for protecting the environment, conserving resources, and promoting sustainable development. By implementing comprehensive waste management strategies and promoting responsible consumption and disposal practices, we can reduce environmental pollution, mitigate climate change impacts, and create a healthier planet for current and future generations. Collaboration among governments, industries, communities, and individuals is crucial to achieving sustainable waste management practices and safeguarding our natural environment.
The worksheet covers the following topics: –
Types of wastes
Waste Management
Landfills
Open dumping
Burning
Composting
The 3 Rs
Waste Management at home
The Explorer’s sheet
This worksheet is designed to help the students learn the concepts and the topics deeply. It encourages the child to think logically and explore the answers.
Some simple home-based activities are shared to encourage the child to do-and-learn.