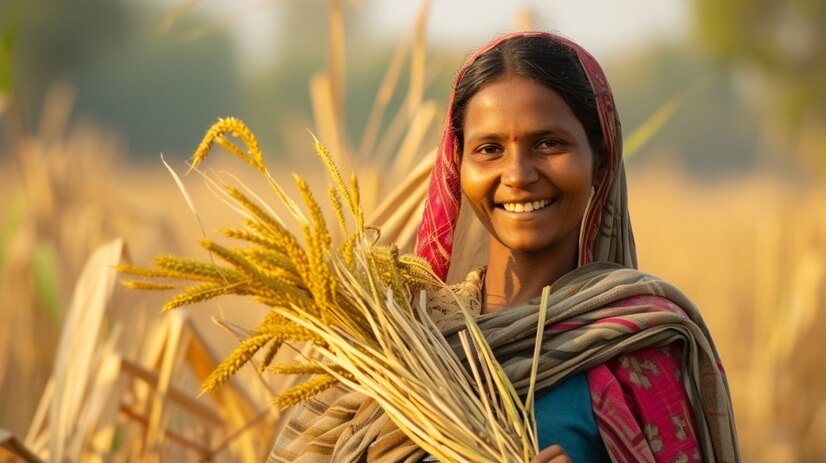
Agriculture is the backbone of India’s economy and a vital aspect of its cultural heritage, providing livelihoods for millions of people across the country. India’s diverse agro-climatic zones, fertile soils, and abundant water resources support a wide variety of crops, making it one of the world’s leading agricultural producers.
From the lush rice paddies of the east to the sprawling wheat fields of the north, and the vibrant spice gardens of the south, Indian agriculture is characterized by its rich diversity. Major crops grown in India include rice, wheat, sugarcane, cotton, pulses, and oilseeds, among others. Additionally, India is a major producer of fruits, vegetables, spices, and tea, contributing significantly to the country’s food security and export earnings.
While traditional farming methods still prevail in many regions, modern agricultural practices, including mechanization, irrigation, and biotechnology, are increasingly being adopted to improve productivity and sustainability. Despite the challenges posed by factors such as land fragmentation, water scarcity, and climate change, Indian agriculture continues to evolve and thrive, driving economic growth, rural development, and food security for the nation.
The worksheet covers the following topics-
Agriculture- Horticulture, livestock rearing and fishing
Types of Crops
Cash Crops- Sugarcane, Jute, cotton, tea, coffee
Agricultural Production
Horticulture
Livestock Rearing
Fishing