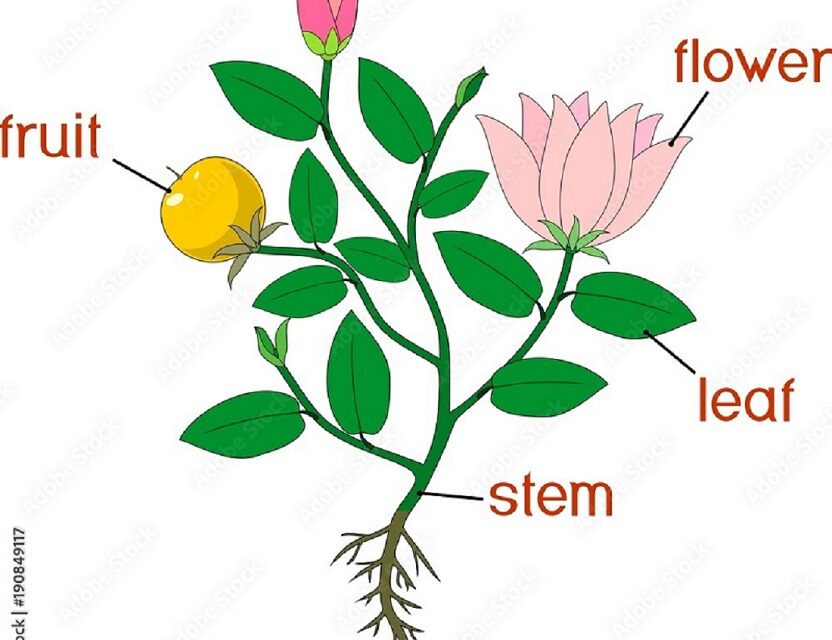
Just like us, plants have different parts that help them live and grow. We’ll learn about each part of a plant, what it does, and how it helps the plant stay healthy. Ready to get started? Let’s dive into the wonderful world of plant parts!
The Root
The root is an important part of a plant that grows underground. It anchors the plant in the soil and helps it take in water and nutrients.
Tap Root
Some plants have a tap root , which is a thick, central root that grows deep into the soil. This root can store food and help the plant stay anchored. Examples of plants with tap roots include:
– Carrot: The orange part we eat is actually a tap root.
– Beet: Known for its round, red root that is also a tap root.
– Dandelion: Has a long tap root that can be difficult to pull out.
Fibrous Root
Other plants have fibrous roots , which are a bunch of thin, branching roots that spread out in all directions. These roots help the plant take up water and nutrients from a large area. Examples of plants with fibrous roots include:
– Grass: The roots spread out to help anchor the grass and absorb water.
– Wheat: Uses fibrous roots to get nutrients from the soil.
– Onion: Has a network of fibrous roots that spread out in the soil.
Functions of the Root
Roots have several important functions:
– Anchoring the Plant: Roots keep the plant stable and upright in the soil.
– Absorbing Water and Nutrients: Roots take in water and minerals from the soil, which are necessary for the plant’s growth.
– Storing Food: Some roots store food and nutrients for the plant, especially during the winter months.
– Supporting the Plant: Roots help support the plant and provide a stable foundation.
The Shoot
The shoot is the part of the plant that grows above the ground. It includes the stem, branches, leaves, and flowers. The shoot helps the plant get sunlight and make food through a process called photosynthesis.
Stem and Their Functions
The stem is like the plant’s “trunk” or “backbone.” It supports the plant and helps transport water, nutrients, and food between the roots and leaves.
– Support: The stem supports the plant and keeps it upright so it can get sunlight.
– Transport: The stem has tubes that carry water and nutrients from the roots to the leaves, and food from the leaves to the rest of the plant.
– Growth: The stem helps the plant grow taller and spread out.
Examples of Stems:
– Tree Trunk: The thick, strong stem of a tree that supports the whole tree.
– Rose Stem: The part of the plant that holds up the flowers and leaves.
– Cucumber Vine: Has a long, flexible stem that can climb up supports.
Branch
Branches are smaller parts that come off the main stem. They help the plant spread out and support the leaves and flowers.
– Support: Branches hold up the leaves and flowers, helping them get more sunlight.
– Growth: Branches allow the plant to grow wider and produce more leaves and flowers.
– Reproduction: Some branches help the plant produce seeds and fruits.
Examples of Branches:
– Tree Branches: Spread out from the trunk to hold leaves and flowers.
– Bush Branches: Grow from the main stem of shrubs to provide extra space for leaves and flowers.
– Vine Branches: Extend outwards to climb and spread across surfaces.
The Leaf and Their Functions
Leaves are the parts of the plant where most of the food-making happens. They come in different shapes and sizes, but they all have similar functions.
Functions of the Leaf
– Photosynthesis: Leaves use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to make food for the plant. This process is called photosynthesis.
– Transpiration: Leaves release water vapor into the air through tiny openings called stomata. This helps cool the plant and move nutrients around.
– Gas Exchange: Leaves take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen, which is important for the plant and the environment.
Examples of Leaves:
– Maple Leaf: Has a unique shape with pointed lobes.
– Oak Leaf: Large and deeply lobed, providing lots of surface area for photosynthesis.
– Cactus Leaf: Reduced to spines to prevent water loss in dry environments.
The Flower and Its Functions
The flower is one of the most colorful and attractive parts of a plant. It plays a key role in reproduction.
Functions of the Flower
– Reproduction: Flowers produce seeds and help plants reproduce. They contain male parts (stamens) and female parts (pistils) that work together to make seeds.
– Attracting Pollinators: Flowers often have bright colors and sweet smells to attract insects like bees and butterflies, which help spread pollen.
– Producing Seeds: After pollination, flowers develop into fruits that contain seeds. These seeds can grow into new plants.
Examples of Flowers:
– Rose: Known for its beautiful, fragrant petals.
– Sunflower: Has large, sunny flowers that turn to face the sun.
– Tulip: Produces colorful, cup-shaped flowers in the spring.
Fruits and Seeds; and Their Functions
Fruits and seeds are the final stages of a plant’s life cycle. They are crucial for spreading and growing new plants.
Fruits
Fruits develop from the flower after fertilization. They protect the seeds and help in their dispersal.
– Protection: Fruits protect the seeds inside from damage and help them stay safe until they’re ready to grow.
– Dispersal: Fruits can attract animals that eat them and then spread the seeds through their droppings. Some fruits have adaptations to be carried by wind or water.
Examples of Fruits:
– Apple: Contains seeds and is eaten by many animals.
– Pumpkin: Has many seeds inside and is often spread by animals.
– Berry: Small, juicy fruits like strawberries and blueberries that are often eaten by birds.
Seeds
Seeds are the next generation of plants. They contain a tiny plant (embryo) and a food supply to help it grow when conditions are right.
– Germination: Seeds need water, warmth, and air to start growing. This process is called germination.
– Nourishment: Seeds contain stored food that helps the young plant grow until it can make its own food.
– Dispersal: Seeds can be spread by wind, water, animals, or even by bursting open.
Examples of Seeds:
– Corn: Large seeds that grow into tall corn plants.
– Sunflower Seeds: Small seeds that grow into tall sunflowers.
– Pea: Round seeds that grow into pea plants.

– Some plants, like the giant sequoia tree, can live for over 3,000 years!
– The smallest flower in the world is the Wolffia, which is about the size of a grain of rice!
– Bamboo can grow up to 35 inches in a single day, making it one of the fastest-growing plants!
The Leaf and Their Functions
Leaves are the parts of the plant where most of the food-making happens. They come in different shapes and sizes, but they all have similar functions.
Functions of the Leaf
– Photosynthesis: Leaves use sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide to make food for the plant. This process is called photosynthesis.
– Transpiration: Leaves release water vapor into the air through tiny openings called stomata. This helps cool the plant and move nutrients around.
– Gas Exchange: Leaves take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen, which is important for the plant and the environment.
Examples of Leaves:
– Maple Leaf: Has a unique shape with pointed lobes.
– Oak Leaf: Large and deeply lobed, providing lots of surface area for photosynthesis.
– Cactus Leaf: Reduced to spines to prevent water loss in dry environments.
The Flower and Its Functions
The flower is one of the most colorful and attractive parts of a plant. It plays a key role in reproduction.
Functions of the Flower
– Reproduction: Flowers produce seeds and help plants reproduce. They contain male parts (stamens) and female parts (pistils) that work together to make seeds.
– Attracting Pollinators: Flowers often have bright colors and sweet smells to attract insects like bees and butterflies, which help spread pollen.
– Producing Seeds: After pollination, flowers develop into fruits that contain seeds. These seeds can grow into new plants.
Examples of Flowers:
– Rose: Known for its beautiful, fragrant petals.
– Sunflower: Has large, sunny flowers that turn to face the sun.
– Tulip: Produces colorful, cup-shaped flowers in the spring.
Fruits and Seeds; and Their Functions
Fruits and seeds are the final stages of a plant’s life cycle. They are crucial for spreading and growing new plants.
Fruits
Fruits develop from the flower after fertilization. They protect the seeds and help in their dispersal.
– Protection: Fruits protect the seeds inside from damage and help them stay safe until they’re ready to grow.
– Dispersal: Fruits can attract animals that eat them and then spread the seeds through their droppings. Some fruits have adaptations to be carried by wind or water.
Examples of Fruits:
– Apple: Contains seeds and is eaten by many animals.
– Pumpkin: Has many seeds inside and is often spread by animals.
– Berry: Small, juicy fruits like strawberries and blueberries that are often eaten by birds.
Seeds
Seeds are the next generation of plants. They contain a tiny plant (embryo) and a food supply to help it grow when conditions are right.
– Germination: Seeds need water, warmth, and air to start growing. This process is called germination.
– Nourishment: Seeds contain stored food that helps the young plant grow until it can make its own food.
– Dispersal: Seeds can be spread by wind, water, animals, or even by bursting open.
Examples of Seeds:
– Corn: Large seeds that grow into tall corn plants.
– Sunflower Seeds: Small seeds that grow into tall sunflowers.
– Pea: Round seeds that grow into pea plants.
The worksheet covers the following topics-
Root
Tap root
Fibrous Root
Functions of the root
Shoot
Stem and their functions
Branch
Leaf and their functions
Flower and its functions
Fruits and Seeds; and their functions