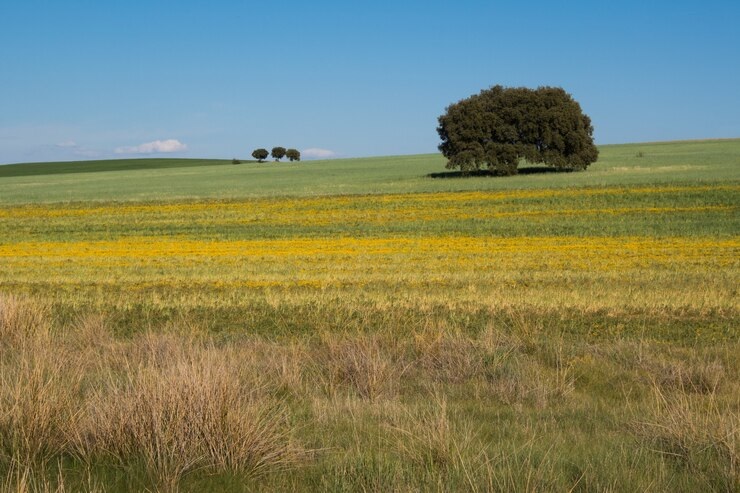
The treeless grasslands known as the Prairies are vast expanses of open plains that stretch across North America, primarily in the central regions of the United States and Canada. These unique ecosystems are characterized by their expansive grassy landscapes, diverse wildlife, and important role in agriculture and the environment.
Geography and Climate:
The Prairies encompass a significant portion of the interior plains of North America, extending from the eastern foothills of the Rocky Mountains to the Mississippi River Valley in the east. They are classified into three main types based on precipitation levels:
- Tallgrass Prairie: Found in regions with higher rainfall, particularly in the eastern part of the Prairies. Tallgrass prairies are characterized by tall grass species such as big bluestem, switchgrass, and Indian grass.
- Mixed-grass Prairie: Located in areas with moderate rainfall, primarily in the central and northern parts of the Prairies. Mixed-grass prairies feature a combination of tall and short grass species, including buffalo grass and blue grama.
- Shortgrass Prairie: Found in drier regions, particularly in the western part of the Prairies. Shortgrass prairies consist of low-growing grass species adapted to arid conditions, such as buffalograss and western wheatgrass.
The Prairies experience a continental climate with hot summers and cold winters. Precipitation patterns vary across the region, influencing the distribution of vegetation and wildlife.
Flora and Fauna:
The grasslands of the Prairies support a rich diversity of plant and animal species adapted to the open plains environment:
– Plant Life: Grasses dominate the landscape, forming dense mats of vegetation that provide food and shelter for wildlife. Wildflowers, such as prairie clover and coneflowers, add splashes of color during the growing season.
– Wildlife: The Prairies are home to a variety of mammals, birds, reptiles, and insects. Iconic species include American bison (buffalo), pronghorn antelope, prairie dogs, coyotes, and various species of birds such as meadowlarks and prairie chickens.
Role in Agriculture:
The fertile soils of the Prairies have made them a significant agricultural region, supporting the production of wheat, corn, soybeans, and livestock grazing. Early settlers recognized the fertility of the prairie soils, leading to extensive farming and ranching activities that continue to this day.
Conservation Challenges:
The Prairies face conservation challenges due to habitat loss, fragmentation, and changes in land use:
– Habitat Loss: Agriculture, urbanization, and energy development have resulted in the conversion of native grasslands into croplands, pastures, and urban areas, impacting wildlife habitats.
– Fragmentation: Fragmentation of grassland habitats isolates populations of wildlife and reduces genetic diversity, affecting their long-term survival.
– Invasive Species: Non-native plants and animals threaten native grassland species by outcompeting native vegetation and disrupting ecosystem processes.
Efforts are underway to conserve and restore prairie ecosystems through habitat restoration, land management practices, and conservation initiatives. Organizations and government agencies collaborate to protect remaining grasslands and promote sustainable land use practices.
Conclusion:
The Prairies represent a unique and ecologically valuable landscape in North America, characterized by expansive grasslands, diverse wildlife, and vital agricultural productivity. Despite facing conservation challenges, ongoing efforts aim to preserve these important ecosystems and their biodiversity for future generations to enjoy and benefit from. Understanding and appreciating the ecological and cultural significance of the Prairies is essential for promoting their conservation and sustainable management in the face of changing environmental pressures.
The worksheet covers the following topics: –
The Prairies
Location
Land
Climate
Vegetation
Wildlife
Economic Activities
Life of the People
This worksheet is designed to help the students to dig deeper into the topics and learn the root cause of the issue. It encourages the child to think logically, explore the answers.
Some simple home-based activities are shared to encourage the child to do-and-learn.